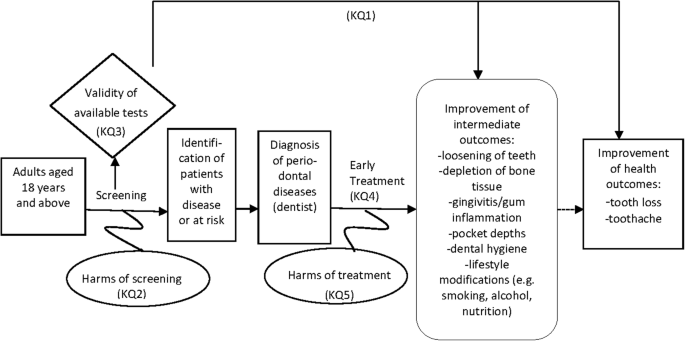
Diagnosis Of Periodontal Disease
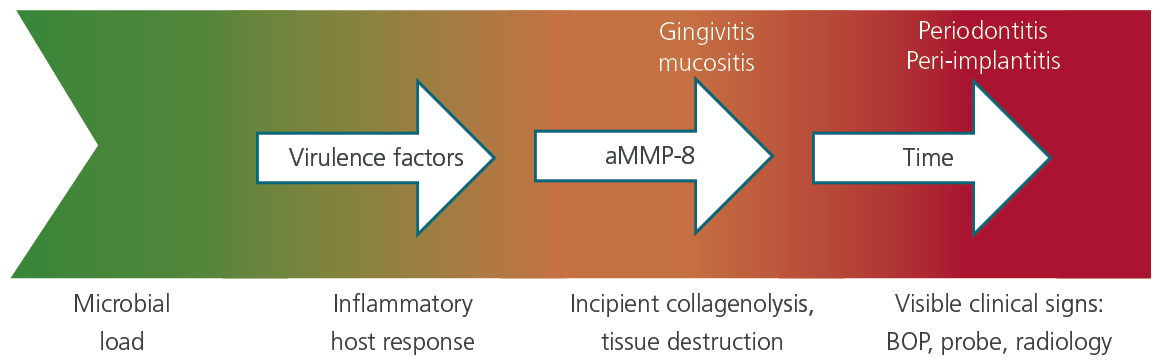
Diagnosis of periodontal disease. Disease2 Clinical diagnosis of periodontal disease is made by the recognition of various signs and symptoms in the periodontal tissues which herald a departure from health. The aim of this study was to identify inflammatory cytokines as salivary biomarkers for periodontal disease. 12 Eight Warning Signs of Periodontal Disease.
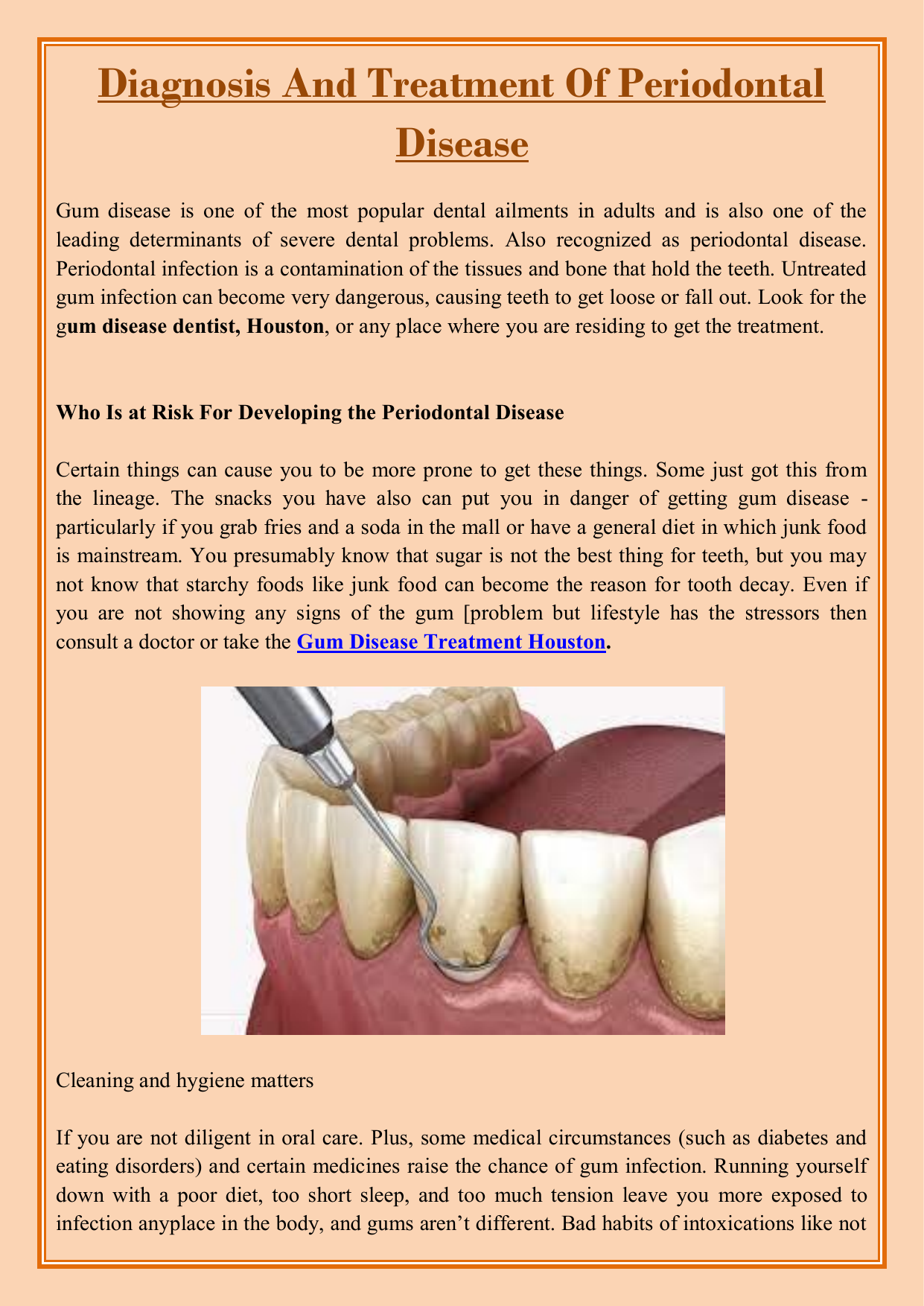
Periodontitis an infectious disease caused by bacteria brings about destructive changes leading to loss of bone and connective tissue attachment Williams 1990. Diseases that appeared in many classification schemes for periodontal diseases in the early 1970s--for example. Diagnosis and classification of periodontal disease body reactions trauma lesions and a catch all not otherwise specified for forms of gingivitis that do not fit.
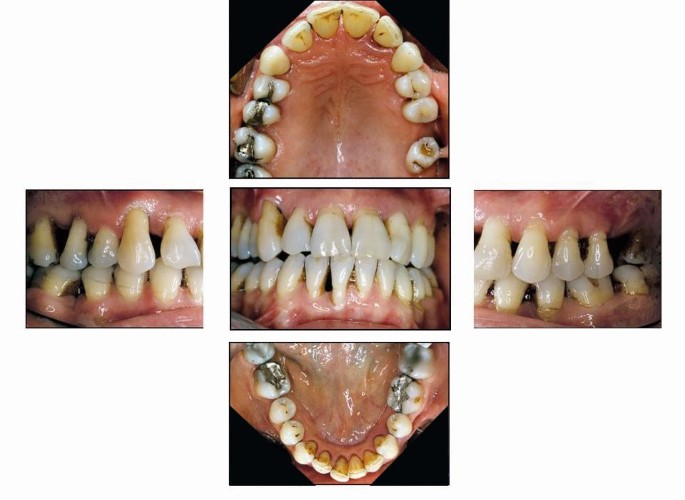
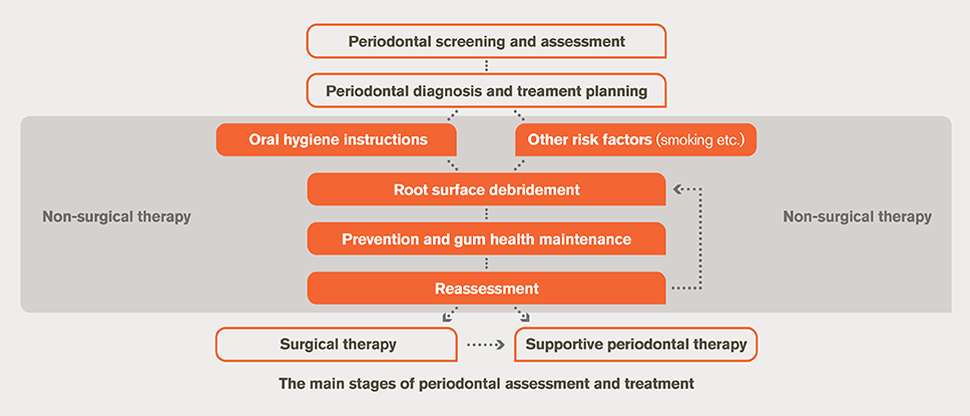
WHAT IS PERIODONTAL DISEASE. This paper reviews current Fall 1990 information related to the diagnosis of periodontal diseases. The diagnosis of periodontal diseases is usually made by a dental practitioner and it includes visual inspection of the gingival tissues the measurement of pocket depth and attachment loss the observation of bleeding upon probing and the evaluation of other clinical parameters such as gingival recession tooth mobility and.
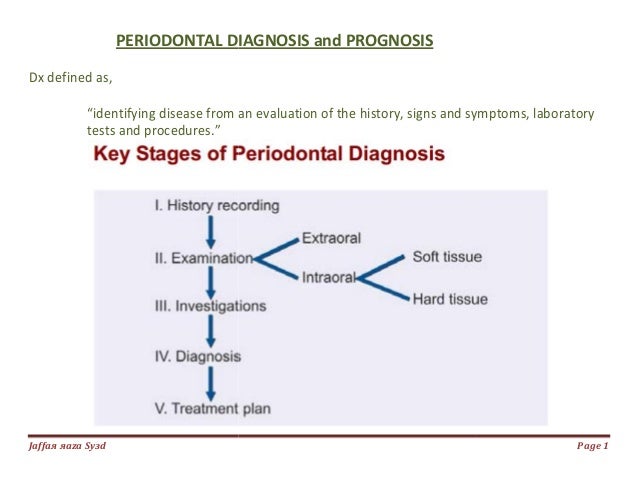
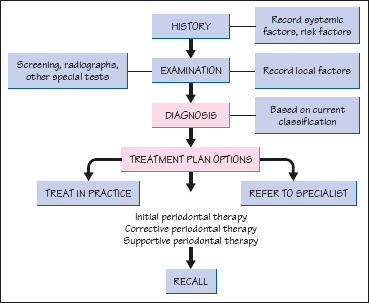
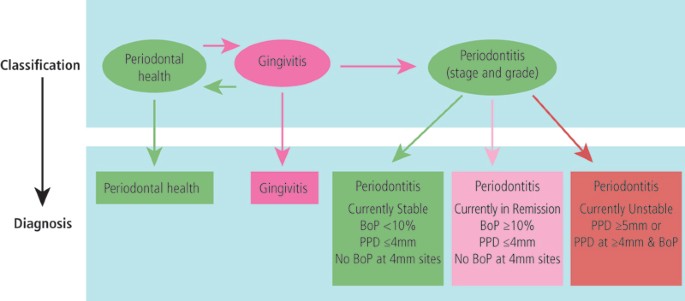
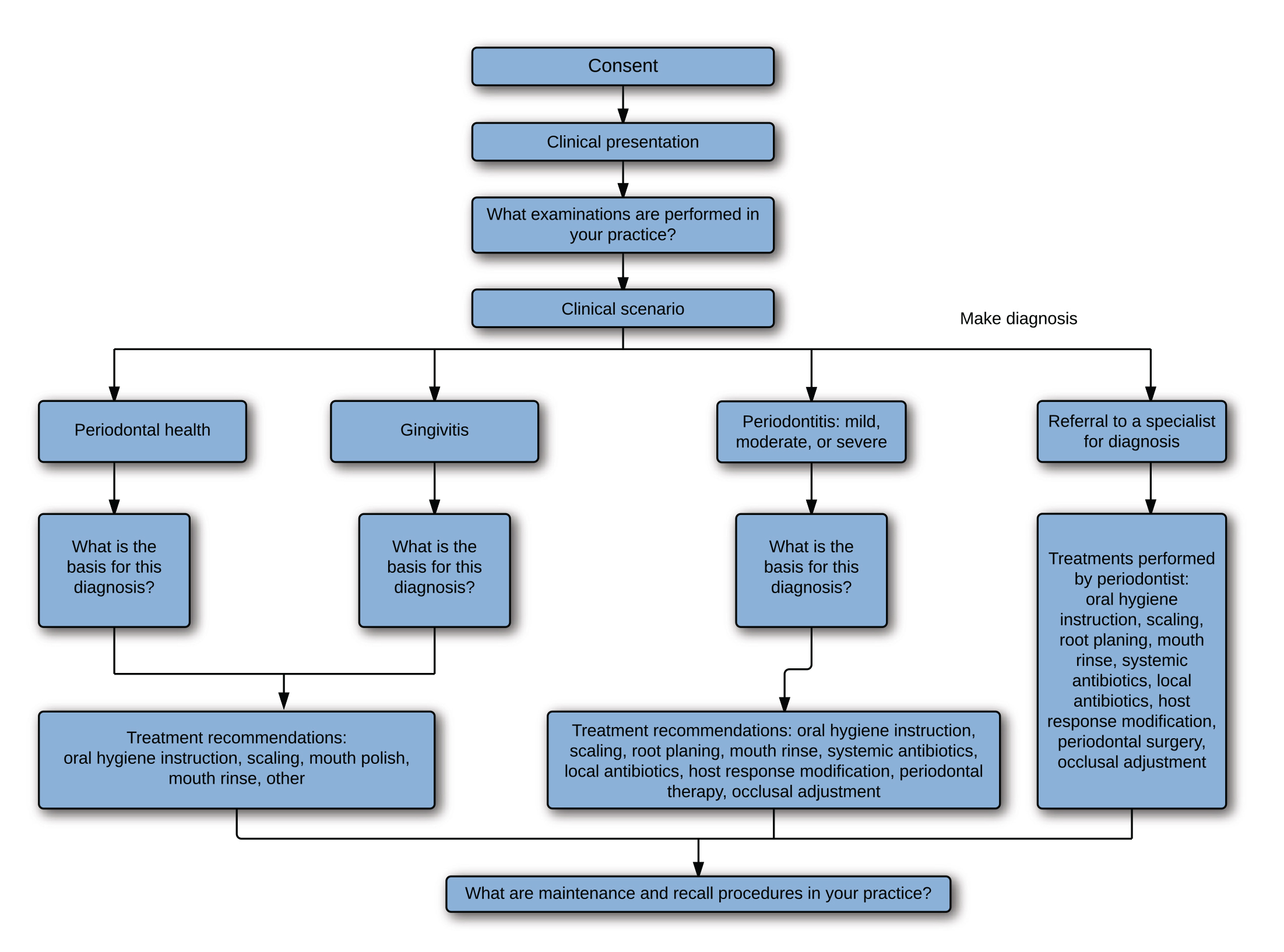
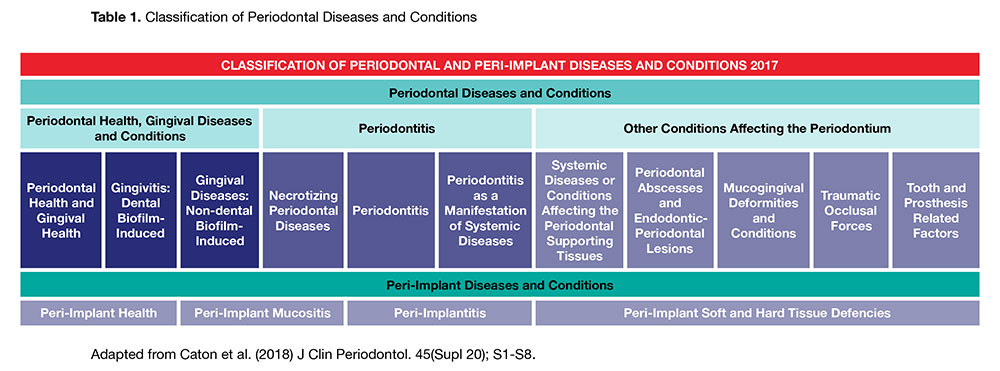
Clinicians use clinical and radiographic findings to diagnose patients according to the classification scheme developed at the 1999 International Workshop for the Classification of Periodontal Diseases and Conditions Table 1. The radiograph is a valuable aid in the diagnosis of periodontal disease determination of prognosis and evaluation of the outcome of the treatment. Diagnosing Periodontal Disease Before any periodontal treatment is undertaken a diagnosis must be made.
To reach a diagnosis the patients dental and medical histories must be taken a clinical examination must be performed and dental x-rays radiographs must be reviewed. Diagnosis of Periodontal Disease Periodontal disease is diagnosed by your dentist or dental hygienist during a periodontal examination. Periodontal disease is destruction of bone and the structures supporting the teeth.
It is an adjunct to the clinical examination not a substitute for it. It is intended for the information of the dental profession and other interested parties. Supplemental quantitative and qualitative assessments of the gingival crevicular fluid and subgingival microflora can potentially provide useful information ab.
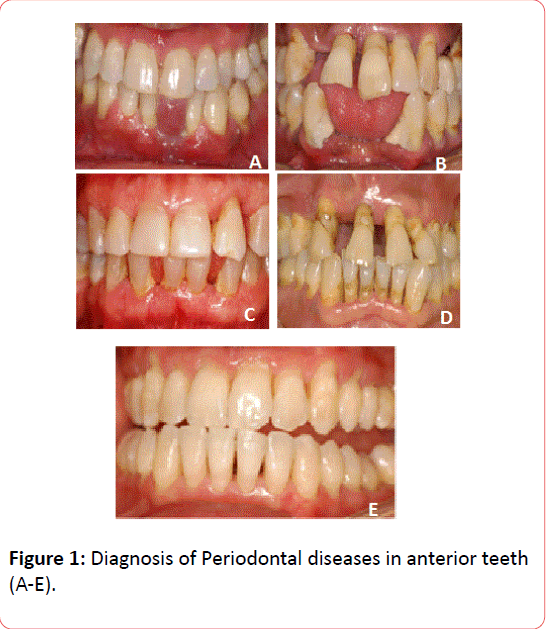
Diagnosis of periodontal diseases. Oral examination for periodontal disease and gingival bleeding was conducted.
The healthy periodontium3 of.
The diagnosis of periodontal diseases is usually made by a dental practitioner and it includes visual inspection of the gingival tissues the measurement of pocket depth and attachment loss the observation of bleeding upon probing and the evaluation of other clinical parameters such as gingival recession tooth mobility and. To reach a diagnosis the patients dental and medical histories must be taken a clinical examination must be performed and dental x-rays radiographs must be reviewed. The diagnosis of periodontal diseases is usually made by a dental practitioner and it includes visual inspection of the gingival tissues the measurement of pocket depth and attachment loss the observation of bleeding upon probing and the evaluation of other clinical parameters such as gingival recession tooth mobility and. Diagnosis is the recognition of the presence of a disease. At the present time the diagnosis and classification of periodontal diseases are almost entirely based on traditional clinical assessments. The radiograph is a valuable aid in the diagnosis of periodontal disease determination of prognosis and evaluation of the outcome of the treatment. The diagnosis of periodontal disease demands a firm knowledge of what constitutes peri-odontal health. Using a multiplexed bead immunoassay called Luminex the levels of inflammatory cytokines related to periodontal disease were evaluated. WHAT IS PERIODONTAL DISEASE.
It is an adjunct to the clinical examination not a substitute for it. The diagnosis of periodontal disease demands a firm knowledge of what constitutes peri-odontal health. Periodontal disease is destruction of bone and the structures supporting the teeth. The aim of this study was to identify inflammatory cytokines as salivary biomarkers for periodontal disease. Using a multiplexed bead immunoassay called Luminex the levels of inflammatory cytokines related to periodontal disease were evaluated. Therefore only a careful clinical examinationcombined with a proper radiographic diagnosing the presence and extent of periodontal disease. Diseases that appeared in many classification schemes for periodontal diseases in the early 1970s--for example.





























Post a Comment for "Diagnosis Of Periodontal Disease"